1. Wi-Fi
ref> http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Wi-fi
- '와이파이' 라고 발음
- Wireless-Fidelity
- Wi-Fi Alliance 에서 만듬
- 무선인터넷 기술의 대표적인 상표
- AP(Access Poing)장치의 주변에서만 동작: 일반 무선인터넷(공유기), Nespot = 쿡앤쇼존
- 802.11a/b/g/n > http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/IEEE_802.11
Wi-Fi
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
The term "Wi-Fi" only applies to only the IEEE 802.11b standard. Wi-Fi (pronounced /ˈwaɪfaɪ/) is a trademark of the Wi-Fi Alliance that manufacturers may use to brand certified products that belong to a class of wireless local area network (WLAN) devices based on the IEEE 802.11 standards. Because of the close relationship with its underlying standard, the term Wi-Fi is often used as a synonym for IEEE 802.11 technology.[1][2]
The Wi-Fi Alliance, a global association of companies, promotes WLAN technology and certifies products if they conform to certain standards of interoperability. Not every IEEE 802.11-compliant device is submitted for certification to the Wi-Fi Alliance, sometimes because of costs associated with the certification process. The lack of the Wi-Fi logo does not necessarily imply a device is incompatible with Wi-Fi devices.
As of 2010[update] an IEEE 802.11 device is installed in many personal computers, video game consoles, smartphones, printers, and other peripherals, and virtually all laptop or palm-sized computers.
2. WIPI
ref> http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/WIPI
- '위피'라고 발음
- Wireless Internet Platform for Interoperablility
- 한국형 무선인터넷 플랫폼 표준규격
- 한국무선인터넷표준화포럼(KWISF)의 표준규격
- 통신 인터넷 개발 플랫폼으로 C와 JAVA를 말함, 국내만 해당
- WIPI(위피)는 한국에서 발매되는 모든 휴대폰에 의무적으로 탑재되어야 하는 표준 규격이다.
하지만 2009년 4월 1일부로 의무적 탑재가 폐지되고 제한은 풀리게 되었다.
그래서 후에 아이폰이 한국에 진출 할 수 있게 된 것이다.
- 이 WIPI(위피)의 제한은 국내시장보호를 목적으로 하는 민감한 사안이다. 하지만 의무는 이제 폐지.
WIPI
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
| Korean name | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
WIPI (Wireles Internet Platform for Interoperability, Korean pronunciation: [wipʰi]; English: /ˈwɪpi/) is a middleware platform used in South Korea that allows mobile phones, regardless of manufacturer or carrier, to run applications. Much of WIPI is based on Java, but it also includes the ability to download and run compiled binary applications as well.
The specification was created by the Mobile Platform Special Subcommittee of the Korea Wireless Internet Standardization Forum (KWISF). The South Korean government had enforced that all cellular phones sold in that country include the WIPI platform to avoid inordinate competition between mobile companies, but the policy is withdrawn from April 2009.
3. WiBro
ref> http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Wibro
- '와이브로'라고 발음
- Wireless Broadband
- 다중접속(CDMA)기술의 응용
- IEEE802.15e 표준에 기반
- 이동중에 무선인터넷을 즐길 수 있는 무선휴대인터넷
- 노트북에 핸드폰 절반사이즈의 단말기를 USB에 꽂아 사용
- 삼성전자와 한국전자통신연구원이 개발
WiBro
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
| WiBro | |
|---|---|
 Wibro Egg sold by KT, produced by Interbro |
|
| Korean name | |
| Hangul | 와이브로 |
| Revised Romanization | waibeuro |
| McCune–Reischauer | waibŭro |
WiBro (Wireless Broadband) is a wireless broadband Internet technology developed by the South Korean telecoms industry. WiBro is the South Korean service name for IEEE 802.16e (mobile WiMAX) international standard.
WiBro adopts TDD for duplexing, OFDMA for multiple access and 8.75 MHz as a channel bandwidth. WiBro was devised to overcome the data rate limitation of mobile phones (for example CDMA 1x) and to add mobility to broadband Internet access (for example ADSL or Wireless LAN). In February 2002, the Korean government allocated 100 MHz of electromagnetic spectrum in the 2.3 - 2.4 GHz band, and in late 2004 WiBro Phase 1 was standardized by the TTA of Korea and in late 2005 ITU reflected WiBro as IEEE 802.16e (mobile WiMAX). Two South Korean Telcom (KT, SKT) launched commercial service in June 2006, and the tariff is around US$30.
WiBro base stations will offer an aggregate data throughput of 30 to 50 Mbit/s per carrier and cover a radius of 1–5 km allowing for the use of portable internet usage. In detail, it will provide mobility for moving devices up to 120 km/h (74.5 miles/h) compared to Wireless LAN having mobility up to walking speed and mobile phone technologies having mobility up to 250 km/h. From testing during the APEC Summit in Busan in late 2005, the actual range and bandwidth were quite a bit lower than these numbers. The technology will also offer Quality of Service. The inclusion of QoS allows for WiBro to stream video content and other loss-sensitive data in a reliable manner. These all appear to be (and may be) the stronger advantages over the fixed WiMAX standard (802.16a). Some Telcos in many countries are trying to commercialize this Mobile WiMAX (or WiBro). For example, TI (Italia), TVA (Brazil), Omnivision (Venezuela), PORTUS (Croatia), and Arialink (Michigan) will provide commercial service after test service around 2006-2007. While WiBro is quite precise in its requirements from spectrum use to equipment design, WiMAX leaves much of this up to the equipment provider while providing enough detail to ensure interoperability between designs.
4. WiMAX
ref> http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Wimax
- '와이맥스'라고 발음
- Worldwide Interoperability for Microwave Access
- Wi-Fi 처럼 근거리 연결과, WiBro처럼 이동중 접속을 혼합(?)
- 다양한 방식(Wi-Fi + WiBro)으로 무선인터넷 접속 가능
WiMAX
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
WiMAX, meaning Worldwide Interoperability for Microwave Access, is a telecommunications technology that provides fixed and fully mobile internet access. The current WiMAX revision provides up to 40 Mbps[1] in real world end-user throughput. WiMAX is based on the IEEE 802.16 standard (also called Broadband Wireless Access). The name "WiMAX" was created by the WiMAX Forum, which was formed in June 2001 to promote conformity and interoperability of the standard. The forum describes WiMAX[2] as "a standards-based technology enabling the delivery of last mile wireless broadband access as an alternative to cable and DSL".[3]
5. WiGig
ref> http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/WiGig
- '와이기그'라고 발음(?)
- Wireless Gigabit
- Wi-Fi보다 10배정도 빠른 동영상 무선전송기술
- 2010년부터 출시 할듯?
Wireless Gigabit Alliance
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
The Wireless Gigabit Alliance[1] (also known as WiGig) is an organization promoting the adoption of multi-gigabit-speed wireless communications technology operating over unlicensed 60 GHz spectrum.
The creation of WiGig was announced on May 7, 2009.[2][3][4][5][6]
Wireless communications systems operating in the 60 GHz band take advantage of the high absorption caused by oxygen, which limits signal propagation to a few feet, thus reducing interference to/from other neighbor wireless systems.[7]
The WiGig specification will allow devices to communicate without wires at gigabit speeds within a typical room.
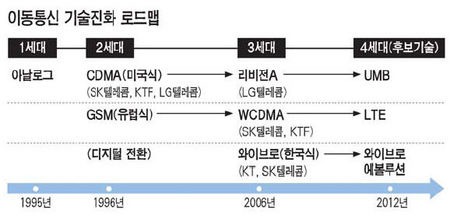
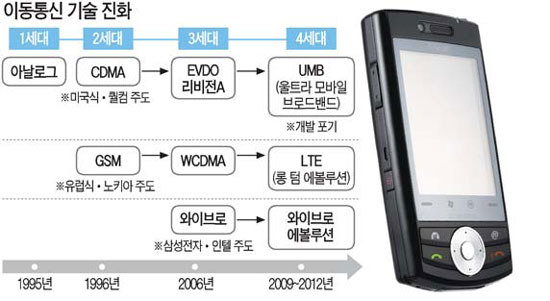
6. 1G/2G/3G/4G/5G
- 'G' is a 'Generation'.
- 'G'는 이동통신의 세대를 말함. (3G = 3세대 이동통신)
1) 1G (1세대 이동통신)
- Analog 기반.
- 아날로그로 기존 옛날 그냥 집전화(for phone in home)
- '음성'만 전송가능(only for sending voice)
2) 2G (2세대 이동통신)
- GSM방식(Europe), CDMA방식(USA/KOREA)
- GSM: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gsm
- CDMA: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cdma
- Digital 기반.
- 2G부터 Digital로 전환
- '음성/문자'만 전송가능(for sending voice and text)
- 많이 들어본 PCS폰이 CDMA방식(부호분할다중접속)
3) 3G (3세대 이동통신)
- UMTS방식(W-CDMA,Europe), CDMA2000방식(USA), WiBro(KOREA)
- UMTS: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Umts
- CDMA2000: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cdma2000
- 한국(KOR)의 W-CDMA 방식은 KTF의 SHOW, SKT의 T-LIVE.
- 한국(KOR)의 CDMA2000 방식은 LGT의 OZ. (CDMA2000 1x EV-DO Rev.A)
- 국제표준(IMT-2000, International Mobile Telecommunications-2000)
- WiBro도 여기에 포함(including WiBro)
- '음성/문자/영상/이메일' 전송가능(for sending 'Voice, Text, Video, E-mail')
4) 4G (4세대 이동통신)
- UMB방식(Europe), LTE방식(USA), WiBro Evolution(KOREA)
- UMB: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ultra_Mobile_Broadband
- LTE: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/3GPP_Long_Term_Evolution
- UMB는 미국의 퀄컴이 독자개발해온 2008년말에 개발을 포기하고 LTE개발로 전환
(UMB is stopped since end of 2008, and changed to LTE in USA)
- LTE는 유럽의 노키아/에릭슨사의 현재 개발중...
(LTE is deveoping now by NOKIA and ERICKSON(?) in Europe)
- WiBro Evolution은 삼성과 인텔이 개발중...
(WiBro Evolution is developing by Samsung and Intel.)
- 결국 남은건... LTE방식과 WiBro Evolution방식.
(So, There is only Two Case. LTE and WiBro Evolution)
- 5초만에 영화 한편(700MB)을 내려받음
(can download a movie in 5 sec.)
- 2011년후에 상용화 예정
(will show up after 2011.)
- '모든것=Everything' 전송 가능
(for sending everything)
5) 5G (5세대 이동통신)
: 5G는 개인적으로 상상하여 쓴 것입니다.
(5G is in my personal imagination.)
- 2017~2020년정도 상용화 추측
(can show up in 2017 to 2020.)
- 영화에나 나올법한 '입체 3D 화상통화'
(Video-Call by 3D.)
- 기존 시각/청각만 전송하던 것에서 진화해, 질감(촉각)/맛(미각)/냄새(후각)까지 전송
(can send the five senses as video, voice, taste, feel of a material, smell.)
- 질감/맛/냄새는 7G~10G가 되어야 가능할지도...;
(can send taste, feel of a material, smell after 7G to 10G.)
- 향후 10G에는 사물을 전송
(can send a material things after 10G.)
- 향후 15G에는 사람을 전송하여 시간을 초월하는 타임머신 형태라고 추측 -_-;;
(can send a person like Time-Machine after 15G.)
- 3G가 나오기까지 약 12년 정도가 걸린 것 같으니... 7G는 2025~2035년
(Will show up 7G in 2025 to 2035?)
- 10G는 2035~2045년, 15G는 2050~2070년을 예상해봄
(Will show up 10G in 2035 to 2045? and 15G in 2050 to 2070?)
※ 참고 사이트 (Ref. Site)
http://cafe.naver.com/profeel.cafe?iframe_url=/ArticleRead.nhn%3Farticleid=114
http://blog.naver.com/leebhharuki?Redirect=Log&logNo=90051425321
http://www.hankyung.com/news/app/newsview.php?aid=2008111414901
※ 개인적으로 작성한 것이니, 오류가 있을 수도 있음을 알려드립니다.
※ Written for personal blog, So there can be existed with some ERROR. Remind it.
'◆ 무한한 가능성' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [조언] 사수 없으신 신입분들에게 드리는 글. by 판교 (0) | 2013.08.07 |
|---|---|
| 자료구조-알고리즘 좋은 사이트 (0) | 2010.12.20 |
| 다락방서버 (0) | 2010.04.01 |
| Tortoise SVN Client Settings for passing ID and PW. (0) | 2009.10.05 |
| IP 국가대역 정보 알아내기 (0) | 2009.09.24 |
